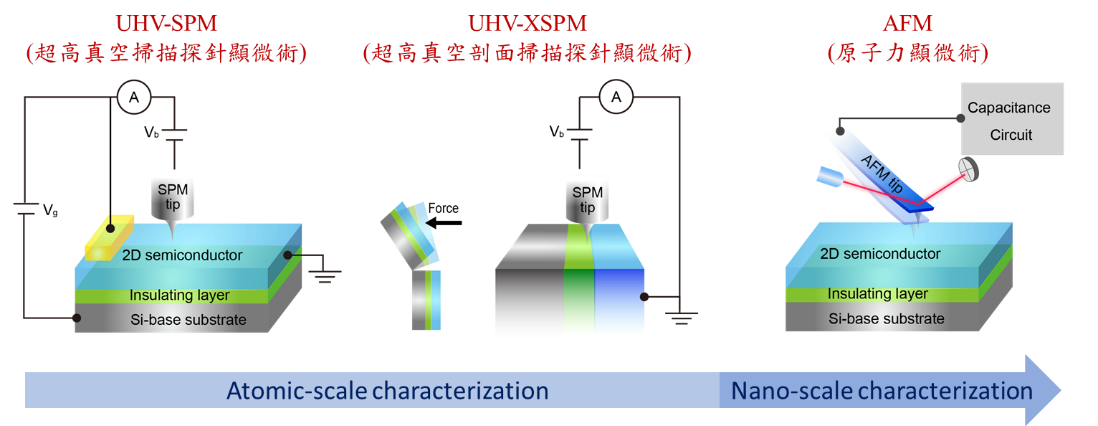
執行現況與成果
尖端掃描探針顯微技術檢測前瞻半導體材料元件關鍵特性
主持人
共同主持人
成功在單層二硫化鉬上進行二階段摻雜,並透過掃描穿隧顯微鏡影像確認摻雜結果。摻雜後的二硫化鉬載子濃度達到4.1×10^13 cm^(-2),導電率高達0.16 mS·〖sq〗^(-1),並且與金的接觸電阻降低至1.2kΩ⋅μm。相關研究成果已被刊登於國際知名學術期刊《ACS Nano》中:“Hysteresis-Free Contact Doping for High-Performance Two-Dimensional Electronics”, ACS Nano 2023 17 (3), 2653-2660.。一般的接觸摻雜技術雖能解決半導體與金屬接面的接觸電阻,但無法應用於二維材料上。此二階段摻雜技術透過缺陷修補式摻雜過程,能夠提供在二維材料上進行高濃度的無遲滯接觸摻雜,同時能夠保持材料的高度載子遷移率並達成高導電率,可有效降低二維半導體的接觸電阻,讓二維半導體能夠實際運用於半導體元件如場效電晶體等。此技術能廣泛適用於過渡金屬二硫族化物。
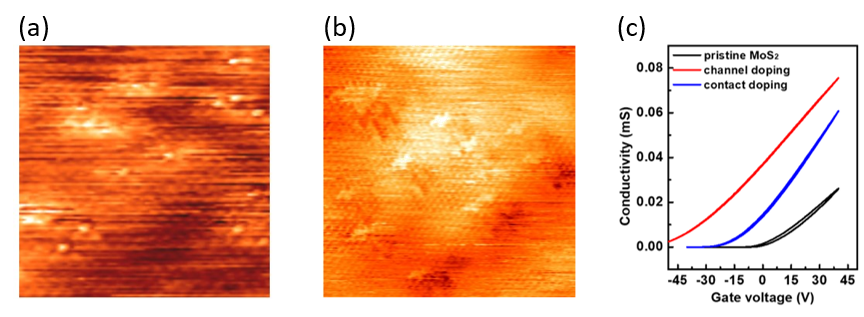
(a) STM image of pristine MoS2 on the SiO2 substrate. Small white spots are the sulfur vacancy sites.
(b) STM image of the two-step-doped MoS2. The white double-cross shapes are the regions with dopants on top of the MoS2.
(c) Gate-dependent characteristic of pristine, channel-doped, and contact-doped MoS2.
團隊利用掃描穿隧顯微鏡與能譜技術成功觀察準粒子干涉現象,並進一步於非光照和光照條件下之實驗結果中,提供光誘導能帶重整化發生於動量禁止電子量子態的直接證據。團隊拓展局限於角分辨光電子能譜和其他光學技術之限制,並提供探索二維過渡金屬二硫族化物中動量禁止能谷量子態自由度之嶄新技術。相關傑出研究成果,已被刊登於國際知名學術期刊《ACS Nano》中:“Directly Visualizing Photoinduced Renormalized Momentum-Forbidden Electronic Quantum States in an Atomically Thin Semiconductor” ACS Nano 2022 16 (6), 9660–9666.。
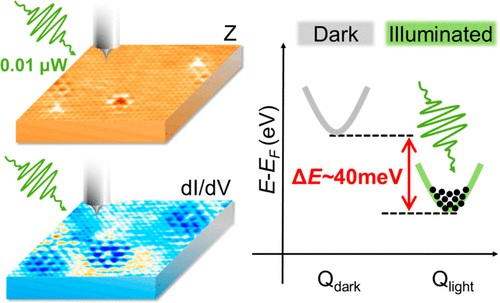
(a) The STS map corresponds to thescanning region on the topographic picture and reveals the QPI patterns in real space.
(b) The schematic diagram of the energy renormalization effect on the Q valley from the photoexcited carriers’ occupation.
Ref.: ACS Nano 16 (6), 9660–9666 (2022).